Wireframing and prototyping are important steps in designing user interfaces (UI) and user experiences (UX). They allow designers to plan, test, and improve their ideas before making the final product. This guide will explain the steps of wireframing and prototyping, and share tools, techniques, and tips to help you along the way.
What are Wireframes ?
Wireframes are simple sketches or drawings that show the basic outline of a design. They highlight the arrangement and structure of different parts of a design without worrying about colors, fonts, or detailed graphics. Think of wireframes as the rough draft or blueprint of your design, showing where things like buttons, images, and text will go on a screen.
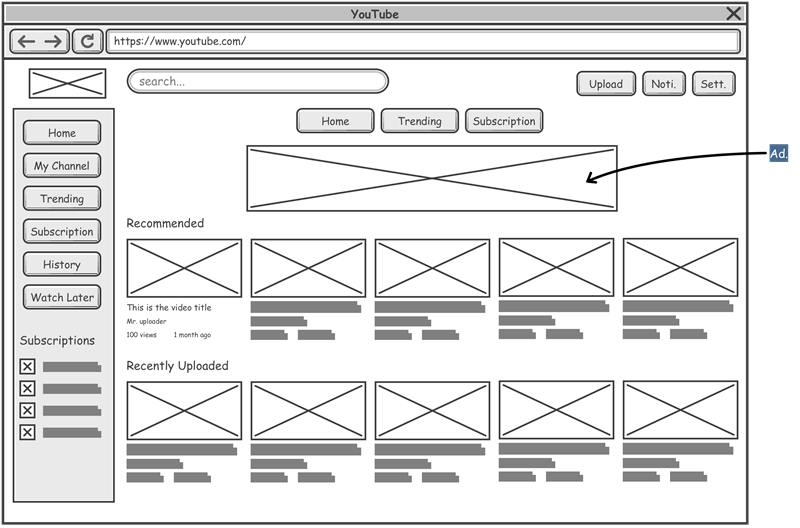
Why Use Wireframes ?
- Clarifies Structure: Helps you arrange content and create a clear order of importance.
- Facilitates Communication: Gives a visual tool to discuss with team members and stakeholders.
- Saves Time and Resources: Finds possible problems early in the design process, preventing costly changes later.
Tools for Wireframing
- Sketch
- Figma
- Adobe XD
- Balsamiq
- Axure RP
Steps to Create Wireframes :
1. Understand User Needs and Goals
Before you start wireframing, it's essential to understand the users' needs and the goals of the project. Conduct user research, gather requirements, and define user personas.
2. Sketch Basic Layouts
Begin with hand-drawn sketches or use a digital tool to create rough layouts. Focus on the placement of major elements such as headers, footers, navigation menus, and content areas.
3. Define Content Hierarchy
Establish a clear hierarchy to guide users through the interface. Decide which elements are most important and should be emphasized.
4. Create Low-Fidelity Wireframes
Using a wireframing tool, create low-fidelity wireframes. These should be simple, with no colors, images, or detailed typography. Concentrate on the structure and layout.
5. Iterate and Refine
Review your wireframes with stakeholders and users. Gather feedback and make necessary adjustments. Iterate until you have a solid structure that meets the project's goals.
What are Prototypes ?
A prototype is like a detailed model of your idea or product. It looks and works almost like the final version. Prototypes let you try out how things will work and see if users can use them easily. They help you find and fix problems before making the real product.
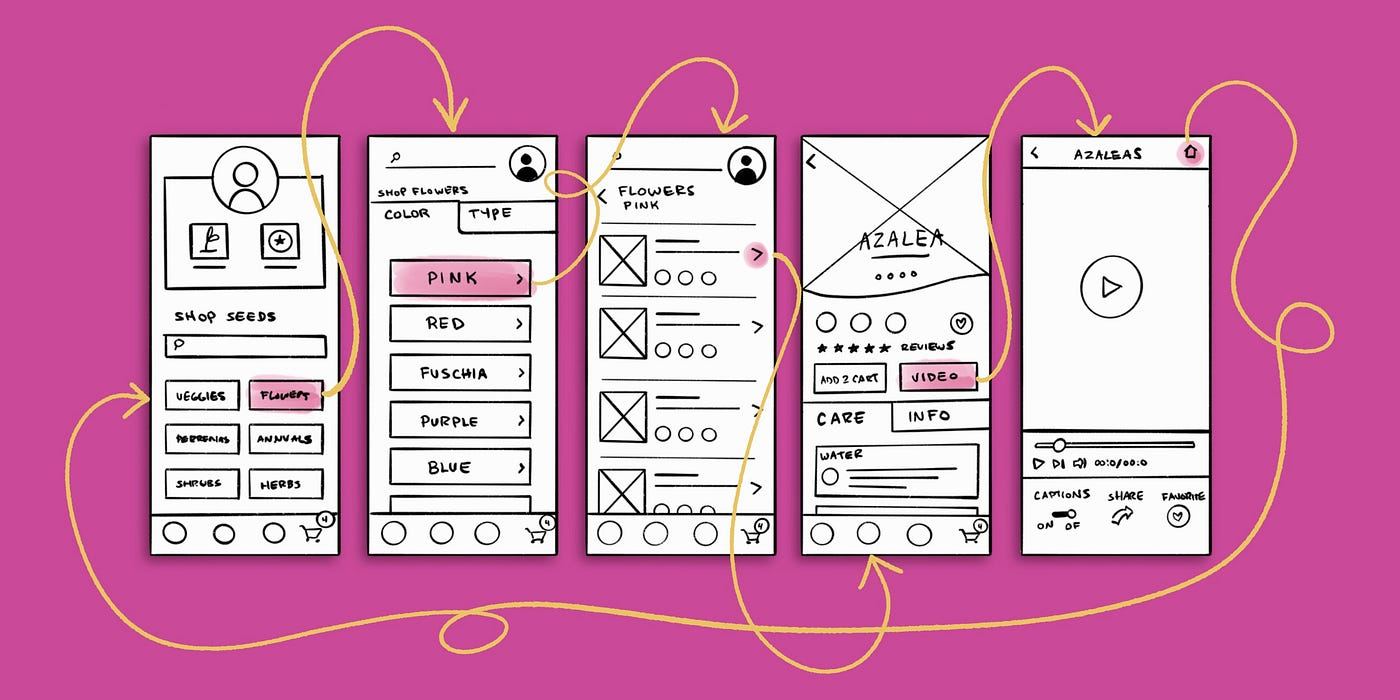
Why Use a Prototype ?
Checks if Ideas Work: Helps you see if your design is practical and easy to use.
Gets Everyone Involved: Gives a clear picture of what the final product will look like, so everyone can understand it.
Finds Problems Early: Spots any issues with usability before you start building the real thing.
Tools for Prototyping
- InVision
- Figma
- Adobe XD
- Axure RP
- Marvel
Simple Steps to Create Prototypes :
1. Start from Wireframes
Use your basic wireframe sketches as the starting point for your prototype. Bring these into a prototyping tool or create detailed versions within the tool.
2. Add Visual Design
Add colors, fonts, images, and icons to your prototype. Make sure the design matches your brand's look and feels visually appealing.
3. Set Up Interactions
Define how users will interact with your prototype. This includes adding actions like clicks, swipes, and animations. Aim for a user-friendly and smooth experience.
4. Test with Real Users
Have actual users try out your prototype. Watch how they use it and note any difficulties or confusion they encounter. Collect their feedback for improvements.
5. Refine and Improve
Use the feedback from testing to make your prototype better. Keep testing and refining until it works well for users and meets your project goals.
Best Practices for Wireframing and Prototyping
- Keep it Simple: Begin with basic designs to concentrate on the overall structure and layout without getting bogged down in details.
- Be Consistent: Use the same design elements and interaction patterns throughout to create a cohesive look and feel.
- Collaborate: Work with team members and users from the start to get valuable input and insights.
- Test Early and Often: Run usability tests at different stages to find and fix problems early on.
- Document Feedback: Keep a record of all feedback and changes made during the design process to track progress and decisions.
Conclusion
Wireframing and prototyping are important parts of creating a good user interface (UI) and user experience (UX). They allow you to see and try out your ideas before fully building them, which can save time and money. This guide will help you through the process, showing you the best ways to create designs that are easy to use and meet your project's goals.
